Pharmaceutical companies and clinical study organizations recognize Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) as extremely vital. They are critical not only to drug development and other related research processes but to patients’ safety as well. In this regard, sustaining quality, precision and compliance is a way to guarantee that pharmaceuticals and medicinal products are safe to use, while human subjects are protected from various trial risks. Therefore, sponsors who are responsible for Quality Assurance and Quality Controll utilize a number of strategies based on FDA and EMHA guidance and principles in order to maintain accuracy and quality throughout the whole course of clinical trials. And one of the most important aspects here is risk management.
What is risk management?
Before explaining risk management, it’s important to clarify what risk stands for. Citing the ISO 31000 standard, risk represents positive or negative “effect of incertitude on objectives”.
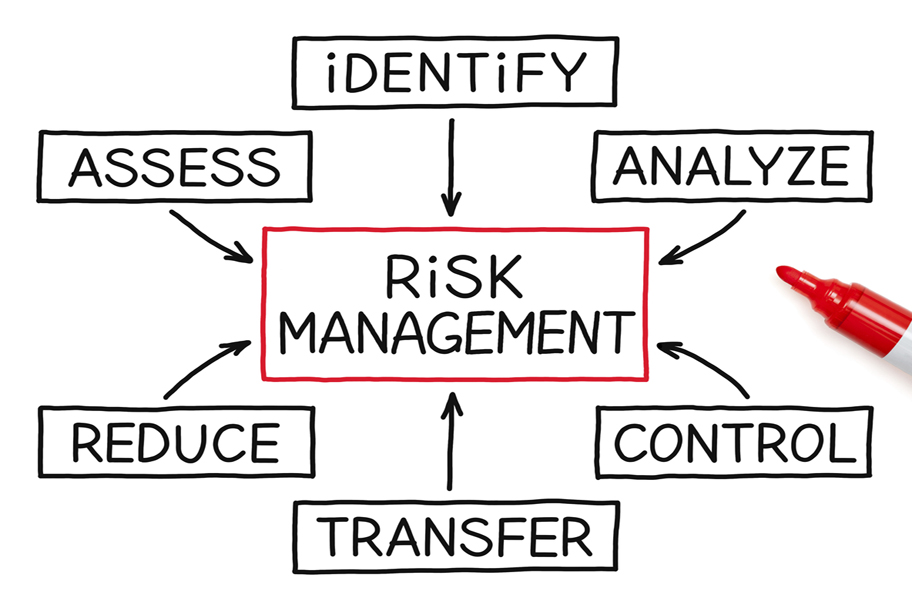
In essence, risk management can be explained as a set of techniques, actions, plans and synchronized activities designed to help practitioners assess, monitor, prevent or mitigate any life- or quality-threatening factors and risks. An effective risk management process is based on several key steps. They begin from the process of comprehending the nature of the risk, go through determining its possible effects and reach stages when practitioners involved take actions to eliminate and mitigate the identified risk.
Precisely, the steps include:
- Methodical adoption of core management policies;
- Risk Communicating – where decision makers, regulatory authorities, patients and other personnel involved share information about the nature, consequences, control, acceptability or any other relevant aspects;
- Risk documentation;
- Consulting;
- Setting up the context and planning of resources required for the management of risks;
- Finding, categorizing, analyzing, assessing, describing, treating, monitoring and reviewing risks;
There are important questions to consider when identifying and evaluating risks. These questions are underlined in ICH Q9 and some of them are:
- What might be the aspect/thing/phase/process that may go wrong?
- What is the probability?
- Will it be possible to detect the issue?
- How serious is the issue?
- What is the scope of the issue?
- Are there going to be any consequences and what is the severity?
Mitigating the risk depends on the level of the risk itself. What’s important then is to carefully review the risk and find out if it is within the acceptable levels. That will help practitioners make an informed decision as to whether the issue can be reduced or eliminated completely. Another key process here is to share information across departments and teams. The clearer communication is established, the better and quicker the whole process will run. However, it’s not just questions and procedures which deliver effective risk management. Having well-prepared and trained personnel is what promises successful risk management as well.
In this regard, Clinical Risk Managers (CRM) should be familiar with available techniques, methodologies, and the best possible analytical tools in order to conduct appropriate risk management. Some of the tools which can be used throughout the risk identification phase, for example, are process maps, cause diagrams, effect charts and tables, flowcharts and more.
At AstraNova we realize that being experienced, having enough knowledge and getting equipped with the necessary skills is mandatory when it comes to controlling risks and managing them. For this reason, we have created a Clinical Trial Risk Management course which is available online. The training is beneficial to Clinical Investigators, sponsors, regulators, risk management personnel, CRAs, compliance specialists as well as students and academic staff. Divided into several well-structured sections, our Clinical Trial Risk Management course will show you how to put into practice some of the best risk management techniques in clinical trials. It also includes basic principles of risk management, reveals how to document risks, highlights key aspects of ICH Q9 and the regulatory background to risk management.
More about our course agenda, corporate discounts and other information can be found here.
You can find a PDF version of this article here: https://crotraining.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/The-Importance-of-Risk-Management-in-Clinical-Trials.pdf